TLDR: Major airports handling 30-100 million passengers annually face severe labor shortages and demand efficient baggage handling automation. Neousys Technology's rugged embedded computers enable autonomous luggage towing vehicles to navigate busy airfields reliably, processing real-time sensor data while withstanding outdoor temperature extremes, vibration, and 24/7 operation cycles.
Overview: Airport Automation Addresses Critical Labor Challenges
The Growing Need for Automated Baggage Handling
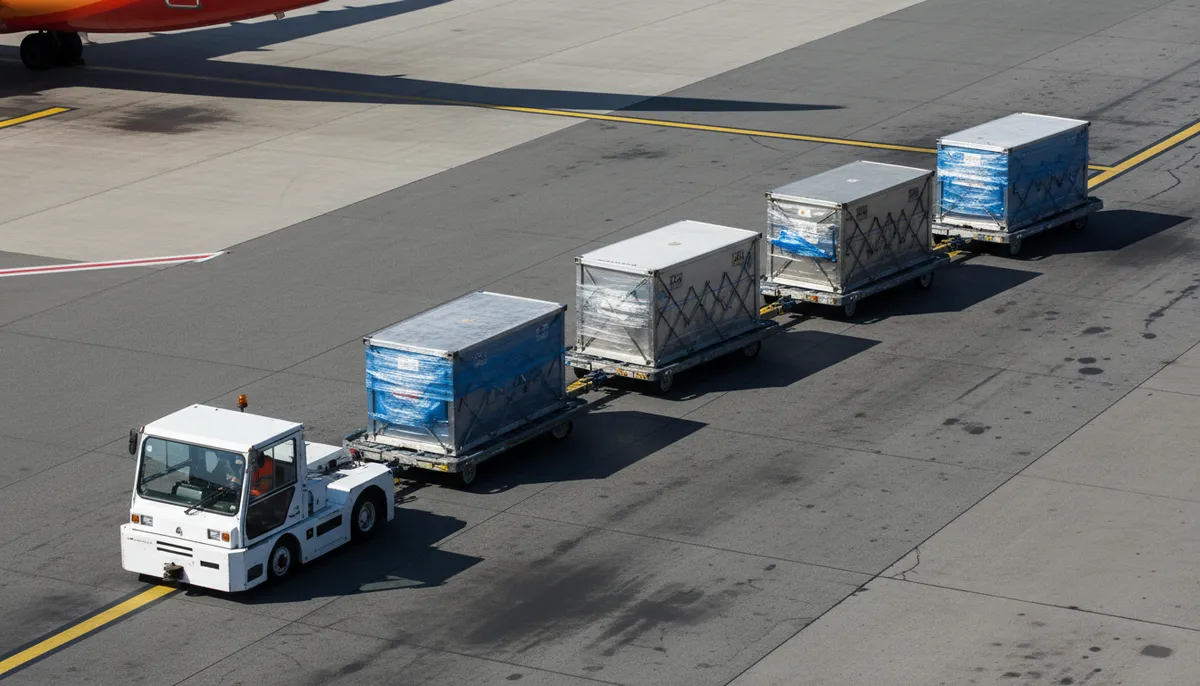
The global aviation industry transports over 4.5 billion passengers annually, with major hub airports like Tokyo Narita, Singapore Changi, and Amsterdam Schiphol processing 30 to 100 million travelers each year. These volumes generate massive baggage handling demands—approximately 5,000 luggage tractors serve airports worldwide, with the largest facilities purchasing hundreds of units annually.
However, the aviation sector faces a critical challenge: severe labor shortages in ground operations. Airside baggage handling requires staff to work outdoors in extreme temperatures, handle repetitive tasks over long distances, and maintain operations across multi-shift schedules. The decline in working-age populations in developed countries has intensified recruitment difficulties, particularly for physically demanding roles like baggage tractor operators.
Autonomous luggage towing vehicles represent a transformative solution. These electric, self-driving tractors navigate between terminals and aircraft stands, transporting baggage carts autonomously while airport staff focus on higher-value tasks requiring human judgment. The automation market is expanding rapidly, with electric tractor adoption growing 15% annually as airports pursue both automation and sustainability goals.
The Core Problem: Computing for Harsh Airport Environments
Deploying autonomous towing vehicles at airports requires embedded computing platforms that can operate reliably in challenging conditions while delivering real-time processing for safe autonomous navigation.
Challenge: Demanding Requirements for Airport Autonomy
Environmental Extremes on the Airfield
Airport tarmacs expose computing systems to harsh outdoor conditions. Temperature variations range from sub-zero winter nights to summer heat exceeding 50°C on sun-exposed asphalt. Humidity from coastal airports accelerates corrosion, while dust and jet fuel fumes contaminate electronic enclosures.
Autonomous tractors operate continuously, often running 16-20 hours daily across multiple charging cycles. Computing platforms must endure constant vibration from towing operations and impacts from uneven pavement, speed bumps, and emergency stops.
Real-Time Autonomy and Safety Requirements
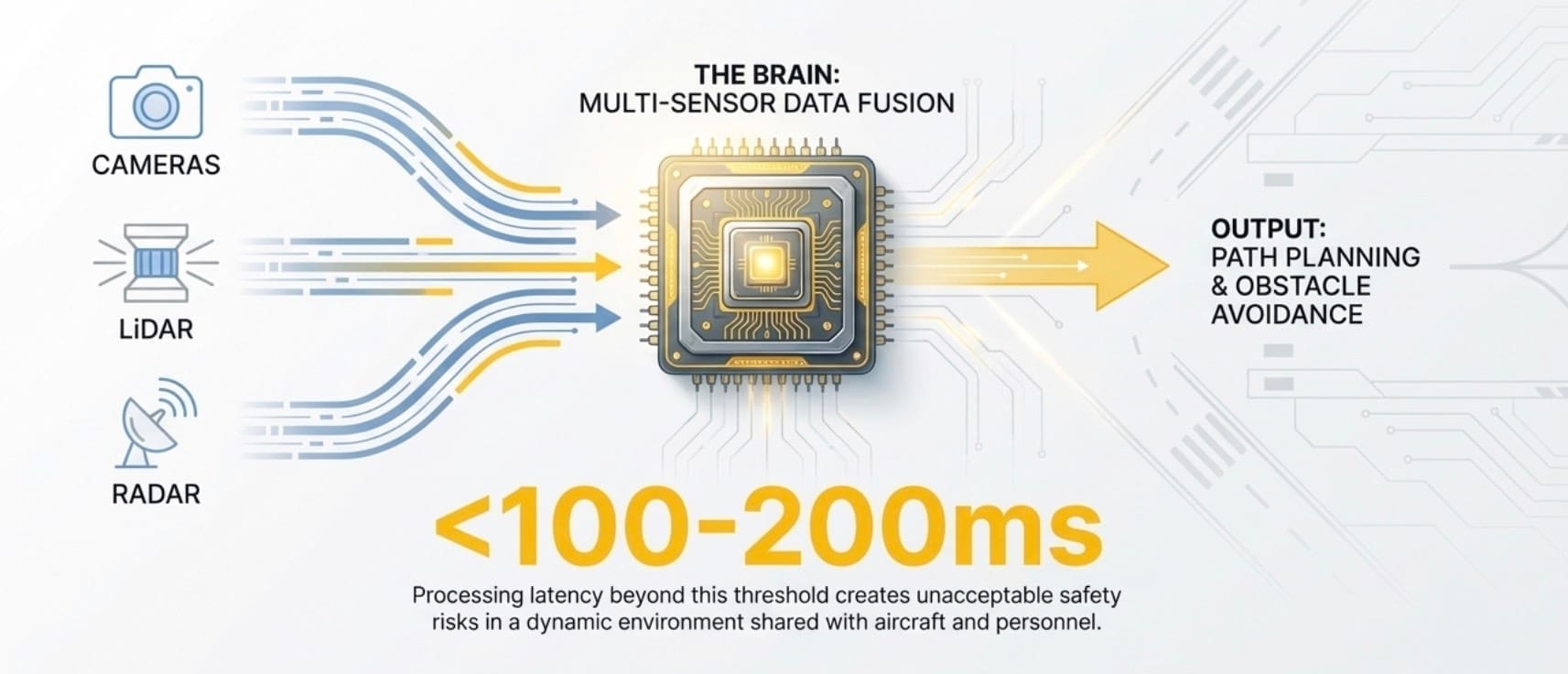
Autonomous luggage vehicles navigate congested airside environments shared with aircraft, service vehicles, and ground personnel. The computing system must process data from multiple cameras, LiDAR sensors, and radar systems simultaneously, executing path planning and obstacle avoidance algorithms in real-time.
Safety regulations demand immediate response to dynamic hazards—stopping within meters when personnel enter the vehicle's path or aircraft begin taxiing. Processing latency exceeding 100-200 milliseconds can create dangerous situations in time-critical scenarios.
Connectivity and Fleet Management
Airport operations require autonomous tractors to communicate continuously with fleet management systems, updating vehicle status, battery levels, and task completion. Wireless connectivity through WiFi or LTE networks enables remote monitoring and route adjustments, but the computing platform must maintain autonomous operation even during network disruptions.
Integration with existing airport infrastructure presents additional complexity. The computer must interface with baggage handling systems, aircraft arrival databases, and security monitoring networks while supporting CAN bus communication for vehicle subsystems.
Compact, Power-Efficient Design Constraints
Electric autonomous tractors prioritize payload capacity and battery range. Computing platforms must fit within tightly constrained spaces, typically alongside batteries, motor controllers, and communication equipment. Size, weight, and power consumption directly impact the vehicle's towing capacity and operational range between charges.
Power efficiency becomes critical—computing systems drawing 50-100 watts reduce battery endurance significantly compared to optimized platforms consuming 15-30 watts while delivering equivalent processing performance.

Solution: Neousys Rugged Computers Enable Reliable Airport Autonomy
Purpose-Built Computing for Autonomous Vehicles
Neousys Technology addresses airport autonomous vehicle challenges through the Nuvo series rugged embedded computers, combining automotive-grade reliability with the I/O flexibility required for complex sensor integration.
The Nuvo-9000 series, powered by Intel 13th/12th Gen Core processors, delivers the computational performance needed for multi-sensor fusion and real-time path planning. Its compact form factor (215mm x 168mm x 69mm) integrates seamlessly into electric tractor chassis while providing sufficient processing power for obstacle detection, mapping, and decision-making algorithms.
For applications requiring AI inference capabilities, the Nuvo-9166GC adds NVIDIA L4 GPU acceleration, enabling advanced computer vision algorithms that identify aircraft, ground vehicles, and personnel with high accuracy even in challenging lighting conditions or adverse weather.
Proven Ruggedness for Continuous Outdoor Operation
Neousys platforms feature fanless thermal designs that eliminate cooling fan failures—a critical vulnerability in dusty, humid airport environments. The patented thermal architecture maintains stable operation from -25°C to 70°C ambient temperature without CPU throttling, ensuring consistent performance during freezing winter operations and summer heat.
MIL-STD-810H shock and vibration certification validates the platforms' ability to withstand continuous towing operations. Screw-lockable connectors and M.2 SSD storage mounting prevent connection failures from vibration, while conformal coating protects circuit boards from moisture and corrosive atmospheres.
The systems achieved UL 62368-1 safety certification, confirming compliance with stringent international safety standards for equipment operating in public airport facilities.
Comprehensive I/O for Vehicle Integration
Neousys computers provide the connectivity required for autonomous towing vehicle deployments:
Sensing and Perception:
- Multiple USB 3.2 ports for LiDAR sensors and cameras
- Gigabit Ethernet ports (up to 5x 2.5GbE + 1x GbE) for IP cameras and radar integration
- Optional PoE+ ports powering network sensors without separate cabling
Vehicle Communication:
- Mini PCIe slots for WiFi 6/LTE/5G wireless modules enabling fleet management
- Isolated CAN bus interface for communication with motor controllers and battery systems
- Digital I/O for emergency stop integration and status indicators
Power Management:
- 9V to 48V DC input handling electric vehicle power delivery
- Ignition power control for automated startup/shutdown synchronized with vehicle systems
- Wide voltage tolerance protecting against electrical transients
Operational Results and Deployment Success
Airports deploying autonomous tractors powered by Neousys computing platforms have achieved significant operational improvements:
Operational Metrics:
- 20-24 hour daily operation across multiple charge cycles
- 99.5%+ uptime in 12-month deployment periods
- Zero weather-related computing failures in outdoor operations
- Sub-50ms sensor processing latency for real-time obstacle avoidance
Singapore Changi Airport's TractEasy autonomous tractors and Cincinnati Airport's Auto-DollyTug deployments demonstrate the technology's maturity, with autonomous vehicles now operating in live airfield environments alongside conventional equipment.
The compact, power-efficient design enables extended range—autonomous tractors complete multiple round-trips between terminals and remote aircraft stands on a single battery charge while maintaining full computing performance.
Related Products: Expanding Autonomous Transportation Solutions
Nuvo-11531 Series: Next-Generation AI Edge Computing
The Nuvo-11531 series powered by Intel Core Ultra 200 processors with integrated NPU delivers up to 36 TOPS AI performance in an ultra-compact form factor. This next-generation platform enhances autonomous vehicle capabilities through:
- Advanced AI-powered predictive maintenance analyzing vehicle health data
- Enhanced computer vision for challenging weather conditions (fog, rain, snow)
- Real-time route optimization considering airport traffic patterns
The integrated NPU offloads AI workloads from the CPU, improving power efficiency and enabling more complex perception algorithms within the same thermal envelope.
Learn more about Nuvo-11531 series
NRU-230V-AWP: Waterproof Edge AI for Outdoor Robotics
The NRU-230V-AWP brings NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin AI acceleration to IP66 waterproof deployments, ideal for autonomous vehicles in extreme weather:
- 275 TOPS AI inference performance for neural network-based navigation
- Native GMSL2 camera support for automotive-grade HDR imaging
- Complete sealing against rain, snow, and high-pressure washdown
This platform enables next-generation autonomous vehicles requiring advanced deep learning capabilities for semantic segmentation, behavior prediction, and complex decision-making in dynamic airport environments.
Explore NRU-230V-AWP capabilities
Nuvo-9650AWP: Water-Resistant Computing for Mobile Applications
The Nuvo-9650AWP provides cost-effective water resistance for autonomous mobile platforms operating in partially exposed environments:
- Intel 14th/13th Gen processors for high CPU performance
- IP55-rated protection against dust and water jets
- Dual M.2 NVMe RAID for secure data logging and map storage
Ideal for autonomous vehicles transitioning between indoor baggage areas and outdoor airfield operations, balancing environmental protection with competitive pricing for large fleet deployments.
View Nuvo-9650AWP specifications
FLYC-300 Series: Lightweight Mission Computing
Though designed for UAV applications, the FLYC-300 series weighing just 300 grams demonstrates Neousys' expertise in ultra-compact, power-efficient computing:
- 100 TOPS AI performance at 25W power consumption
- Wide temperature operation (-40°C to 75°C)
- M.2 NVMe storage and multiple camera interfaces
This technology roadmap informs future autonomous vehicle platforms where size and weight optimization create competitive advantages in payload capacity and energy efficiency.
Conclusion: Powering the Future of Airport Ground Operations
Autonomous luggage towing vehicles are transitioning from trial deployments to operational reality at major airports worldwide. The success of these systems depends fundamentally on rugged embedded computing platforms that deliver reliable performance in demanding outdoor environments while meeting strict safety and operational requirements.
Neousys Technology's proven track record in autonomous vehicle computing—from delivery robots to agricultural machinery to defense systems—positions the company as a trusted partner for airport automation initiatives. The Nuvo series platforms provide the computational foundation enabling airports to address labor challenges, improve efficiency, and advance toward fully automated airside operations.
As electric autonomous tractors become standard infrastructure at global aviation hubs, Neousys continues innovating with next-generation processors, enhanced AI acceleration, and optimized thermal designs to support the evolving demands of intelligent transportation systems.
For airport automation projects, technical specifications, or application engineering support, contact Neousys Technology at www.neteon.net