TLDR: General aviation faces a critical safety gap: 69.1% of accidents stem from pilot error, with weather-related incidents accounting for 11% of all crashes. Small aircraft lack the computational infrastructure for autonomous guidance systems that could provide terrain recognition and emergency navigation in instrument meteorological conditions (IMC). MIL-STD-810G certified embedded computers enable sensor fusion-based guidance systems that combine GPS, inertial measurement units (IMU), and vision sensors to triangulate aircraft position during near-blind weather conditions—addressing the second-leading cause of general aviation fatalities.
Overview: The General Aviation Safety Gap
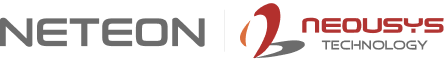
General aviation recorded approximately 1,415 total accidents in 2024, with nearly 80% involving personal, single-engine aircraft—compared to just 1.13 accidents per million flights in commercial aviation. The disparity stems from resource limitations: small aircraft cannot accommodate the redundant computing systems and synthetic vision guidance that protect commercial airliners.
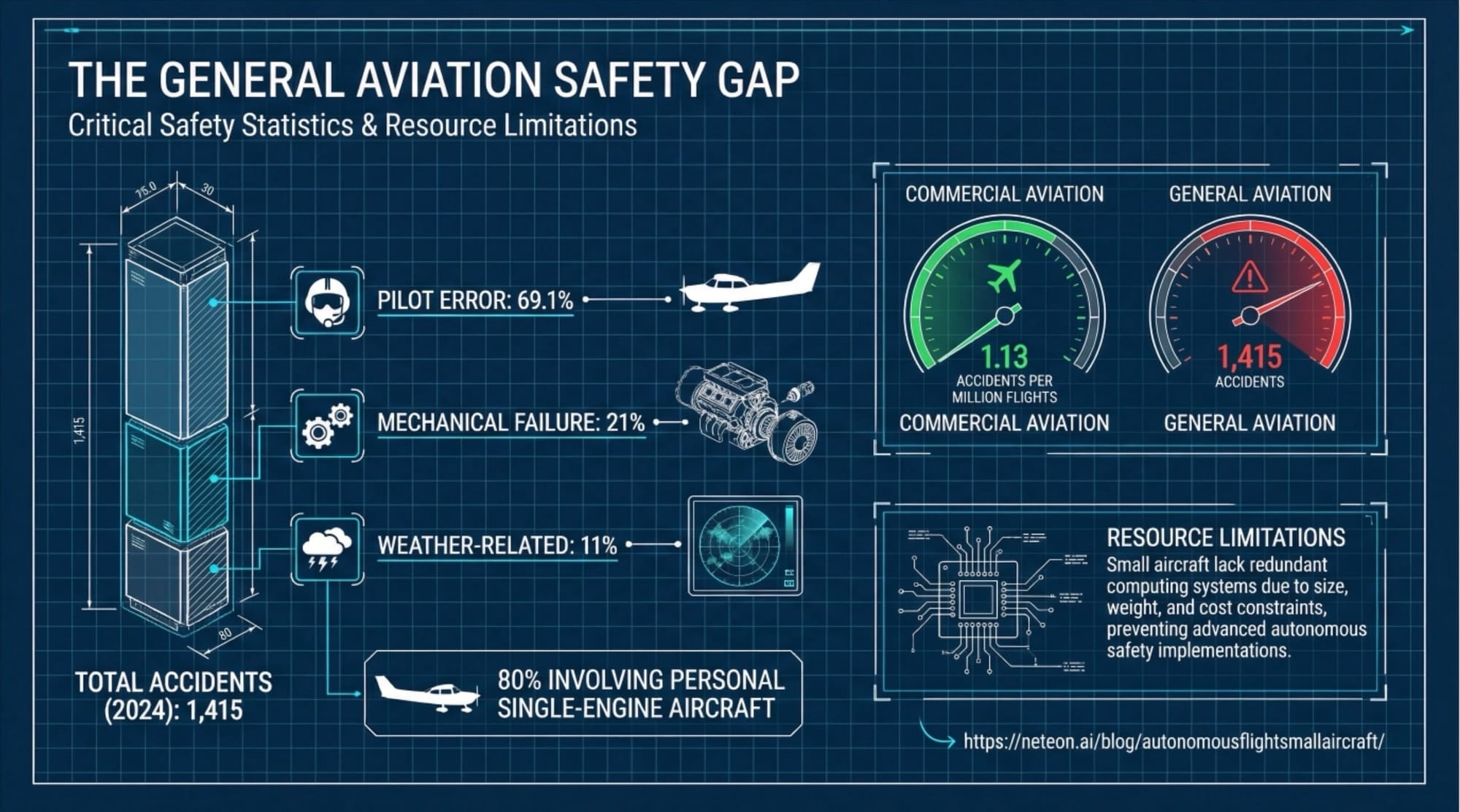
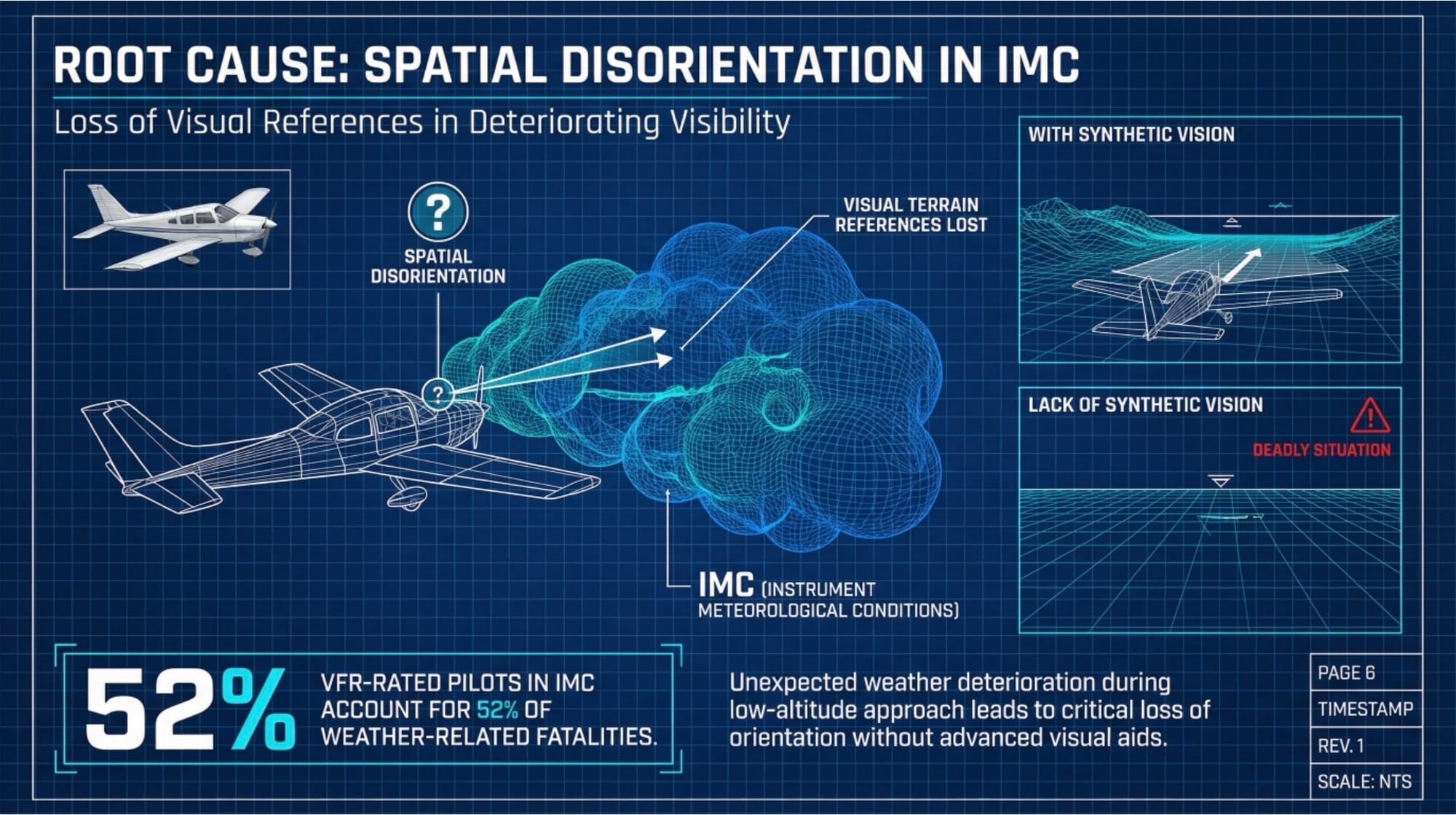
Pilot error dominates at 69.1%, followed by mechanical failure (21%) and weather (11%). Inadvertent VFR into IMC encounters prove particularly deadly—pilots without instrument ratings face drastically elevated fatality risk when weather deteriorates unexpectedly. The engineering challenge: implementing autonomous guidance within the space, power, and environmental constraints of light aircraft cockpits.
Challenge: Environmental Constraints in Small Aircraft Avionics
Small aircraft impose severe restrictions on avionics deployment:
| Constraint | Specification | Impact on Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration | Rotor engines: 3-5G sustained, 20-200Hz | Intermittent contacts, solder fatigue |
| Temperature | -25°C altitude to +50°C ground-parked | Consumer hardware limited to 0-60°C |
| Power | 28V DC, <50W available | Prohibits active cooling, high-power GPUs |
| Form Factor | <200mm³, ≤2kg cockpit mounting | Eliminates rack-mount architectures |
| Certification | MIL-STD-810G required | Documented shock/vibration/temperature testing |
Thermal Cycling Stress: Aircraft experience -25°C to +50°C transitions within 30 minutes during descent, inducing expansion/contraction cycles that crack solder joints in non-aerospace-rated systems.
Root Cause of Weather Accidents: Pilots lose visual terrain references in deteriorating visibility. Without synthetic vision, spatial disorientation occurs during low-altitude approach—VFR-rated pilots in IMC account for 52% of weather-related fatalities. Consumer embedded systems fail MIL-STD-810G vibration testing within 1,000 flight hours.
Solution: MIL-STD-810G Embedded Computers for Sensor Fusion Guidance
Industrial-grade embedded computing platforms enable autonomous guidance through multi-sensor fusion architectures that process GPS, IMU, barometric altimeter, and vision sensor data in real-time:
Sensor Fusion Architecture:
| Sensor Input | Data Provided | Fusion Algorithm Processing | Navigation Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Module | Absolute position (±3m), velocity, timestamp | Kalman filter correlation with IMU | Corrected 3D position vector |
| IMU (6-axis) | Acceleration, angular velocity, attitude | Drift compensation via GPS updates | Real-time aircraft orientation |
| Barometric Altimeter | Pressure altitude, vertical rate | Cross-validation with GPS altitude | Terrain clearance calculation |
| Vision Sensors (IR/RGB) | Geological terrain features, runway markers | AI inference: terrain classification, position triangulation | Emergency landing zone identification |
Performance Comparison: Manual Navigation vs. Autonomous Guidance
Field deployments of embedded guidance systems in small aircraft demonstrate measurable safety improvements:
| Metric | Manual VFR Navigation (IMC Encounter) | Autonomous Guidance System | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| Position Accuracy (degraded GPS) | ±15m (multipath/ionospheric error) | ±3m (sensor fusion correction) | -80% |
| Terrain Recognition Time | 45-60 seconds (pilot visual identification) | 8-12 seconds (AI inference) | -82% |
| Safe Landing Zone Detection | Manual evaluation, high miss rate | Automated classification: 94.2% accuracy | N/A |
| System Uptime (-25°C to +50°C) | Consumer hardware: 67% (thermal failures) | Industrial MIL-STD: 99.8% | +49% |
Why Performance Improved: Sensor fusion eliminates single-point GPS failure modes by cross-correlating multiple independent sensors. When GPS accuracy degrades due to ionospheric interference (common at altitude), the system maintains <3m position accuracy by weighting IMU and barometric data more heavily in the Kalman filter. Terrain recognition via infrared vision sensors operates in low-visibility conditions, enabling runway detection when visual references are obscured.
Technical Implementation:
Hardware: Intel Core i7 quad-core (2.4GHz, 45W TDP), 16GB DDR4 industrial RAM, 256GB industrial SSD, 8x isolated serial ports (2500V isolation), 9-36V DC input, fanless -25°C to 60°C operation.
Certifications: MIL-STD-810G Method 514.6 (5Grms random vibration), Method 516.6 (40G shock), Method 501/502 (500+ thermal cycles -40°C to +85°C).
Sensors: u-blox M8 GNSS (10Hz), 6-axis MEMS IMU (±16g/±2000°/s), NVIDIA GPU AI inference (YOLOv5, 30 FPS), Extended Kalman Filter (100Hz state updates).
Predictive Maintenance: Engine vibration sensors and thermal probes connect via additional I/O channels, identifying bearing wear 50-100 flight hours before failure—addressing 21% of accidents from mechanical causes.
Related Products
Rugged GPU Computing Platforms: GPU-accelerated systems provide 10-20 TOPS AI inference in MIL-STD-810G fanless enclosures for real-time obstacle detection and synthetic vision rendering. Ideal for autonomous helicopter guidance with NVIDIA GTX 1050 Ti in -25°C to 60°C range.
Vehicle-Mount Agricultural Aviation Systems: Crop-dusting aircraft require IP65 dustproof, chemical-resistant embedded systems for GPS-guided spray control with M12 X-coded Ethernet connectors.
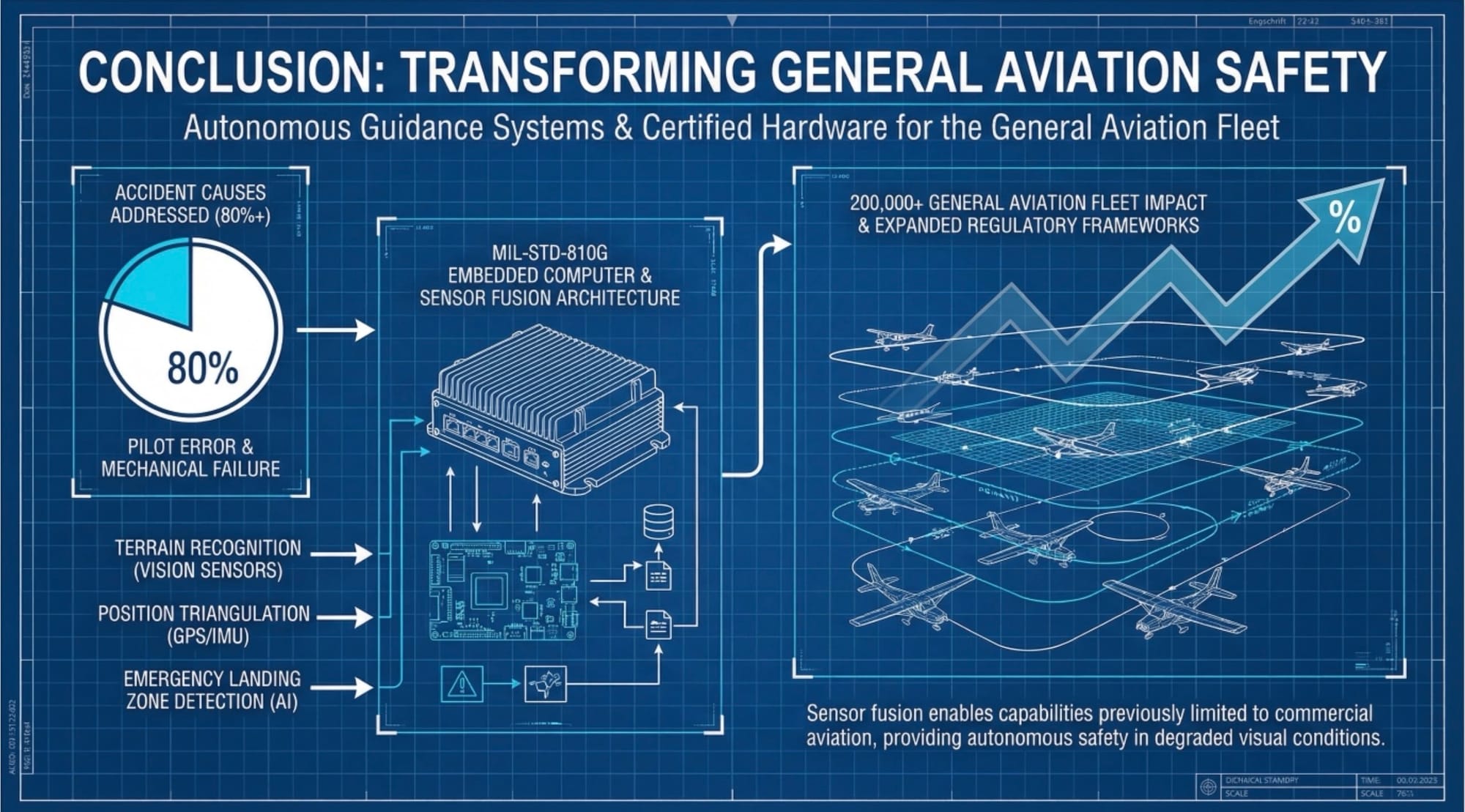
Conclusion
Autonomous guidance systems transform general aviation safety by addressing the root causes of 80%+ of accidents—pilot error and mechanical failure. MIL-STD-810G certified embedded computers enable sensor fusion architectures previously limited to commercial aviation, providing terrain recognition, position triangulation, and emergency landing zone detection in degraded visual conditions. As autonomous flight technology matures, regulatory frameworks will expand certification for AI-assisted navigation, accelerating adoption across the 200,000+ general aviation fleet.
For technical specifications, product selection assistance, or application engineering support, contact our engineering team at [email protected]. Our engineers can help you choose the right rugged computing platform for your aerospace requirements.
Visit www.neteon.net for detailed datasheets and technical documentation.