The Engineering Challenge: Parking Facility Automation Under Continuous Operation
Objective: Modern parking facilities require systems that process vehicle entries and exits continuously without manual intervention, while operating reliably in environments subject to temperature fluctuations, vibration from gate mechanisms, and dust accumulation from constant vehicle traffic.
Traditional parking management evolved from manual toll booth operations to automated token systems. While token-based systems reduced labor costs, they introduced new failure modes: token misplacement resulted in excess fees, and paid tokens could be transferred between vehicles since they contained no vehicle-specific identifiers. These operational inefficiencies created bottlenecks at exit gates and revenue leakage for facility operators.
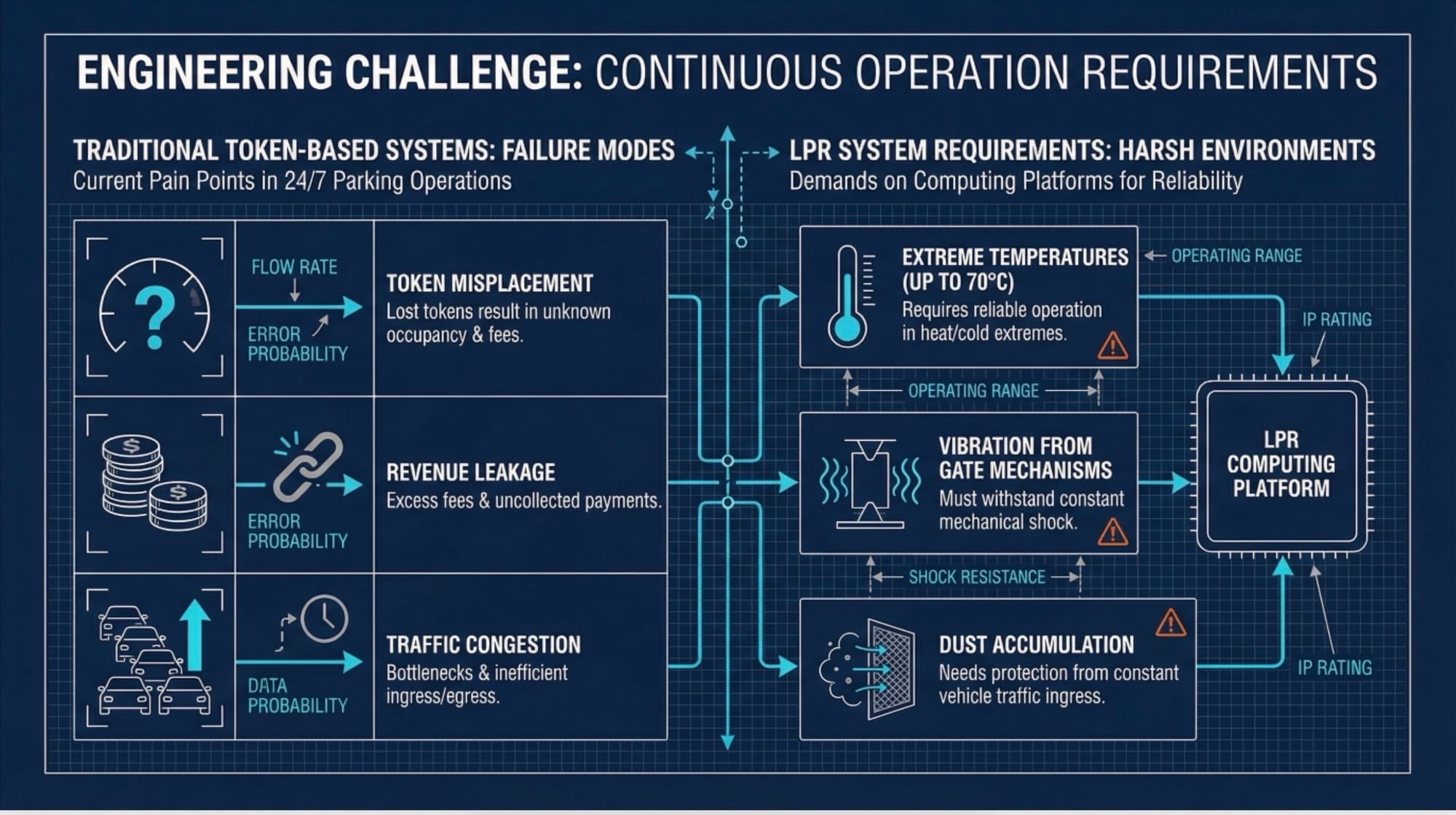
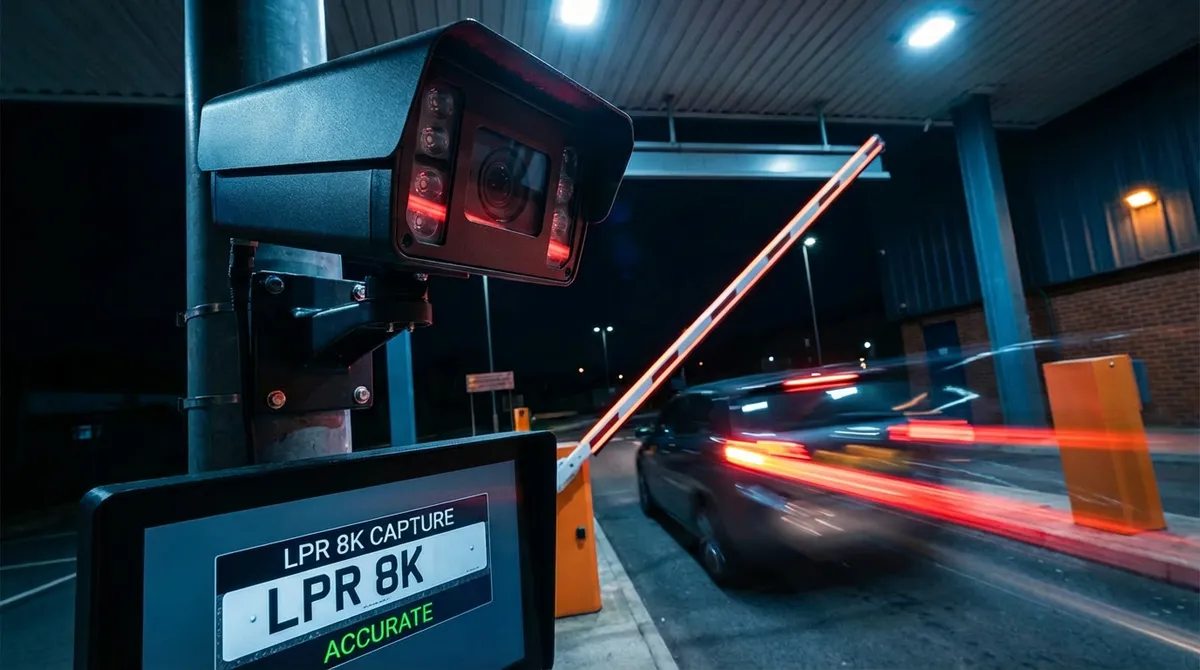
License plate recognition systems address these issues through camera-based vehicle identification, but the computing platforms supporting these vision systems must operate continuously in non-climate-controlled environments where ambient temperatures can reach 70°C near gate equipment and vibration from barrier mechanisms creates mechanical stress on internal components.
Problem Breakdown: Thermal and Mechanical Failure Modes in Parking Infrastructure
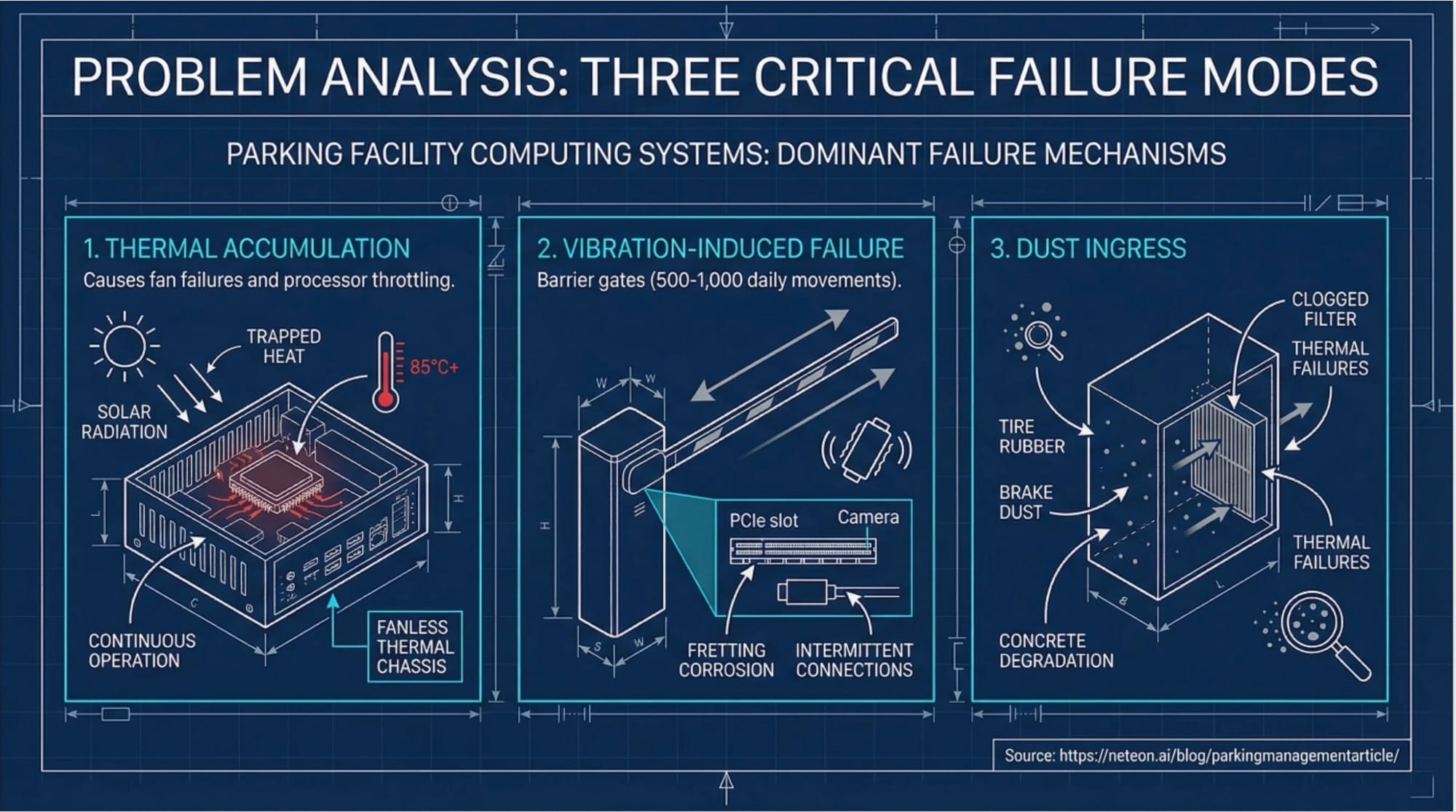
1. Thermal Accumulation: The 24/7 Operation Challenge
Parking facilities operate continuously with no scheduled downtime for maintenance. Computing systems mounted in gate enclosures experience thermal buildup from three sources: internal processor heat generation, solar radiation on metal enclosures, and trapped heat from asphalt surfaces where ambient temperatures routinely exceed 50°C in summer months.
The Failure: Fan-cooled systems experience accelerated bearing wear under continuous operation. When fans fail after 20,000-30,000 hours of runtime, processors throttle performance to prevent thermal damage. This creates cascading failures: slower plate recognition extends vehicle dwell time at gates, increasing queue lengths during peak hours. A single gate with degraded processing performance can reduce facility throughput by 15-20%.
The Architectural Fix: Fanless Thermal Architecture
Nuvo Series embedded computers eliminate active cooling components through three mechanisms:
- Mechanism: Chassis functions as heat sink with extended surface area fins, conducting processor heat directly to ambient air. Thermal interface materials achieve <0.2°C/W junction-to-case resistance.
- Result: Continuous operation at 70°C ambient without performance throttling. Mean time between failures extends beyond 100,000 hours since mechanical components are eliminated.
2. Vibration-Induced Failure: Gate Mechanism Coupling
Barrier gates create repetitive shock loads each time they open and close. A typical parking facility processes 500-1,000 vehicle movements daily, generating mechanical vibration that propagates through mounting hardware to computing equipment.
The Failure: Standard PCIe slots experience fretting corrosion when subjected to repetitive low-amplitude vibration. Gold-plated contacts oxidize as micro-movements break through protective plating, increasing contact resistance over months of operation. Camera interface cards lose connection intermittently, causing frame drops during plate capture. A single missed frame during the critical capture window results in failed identification and manual intervention requirements.
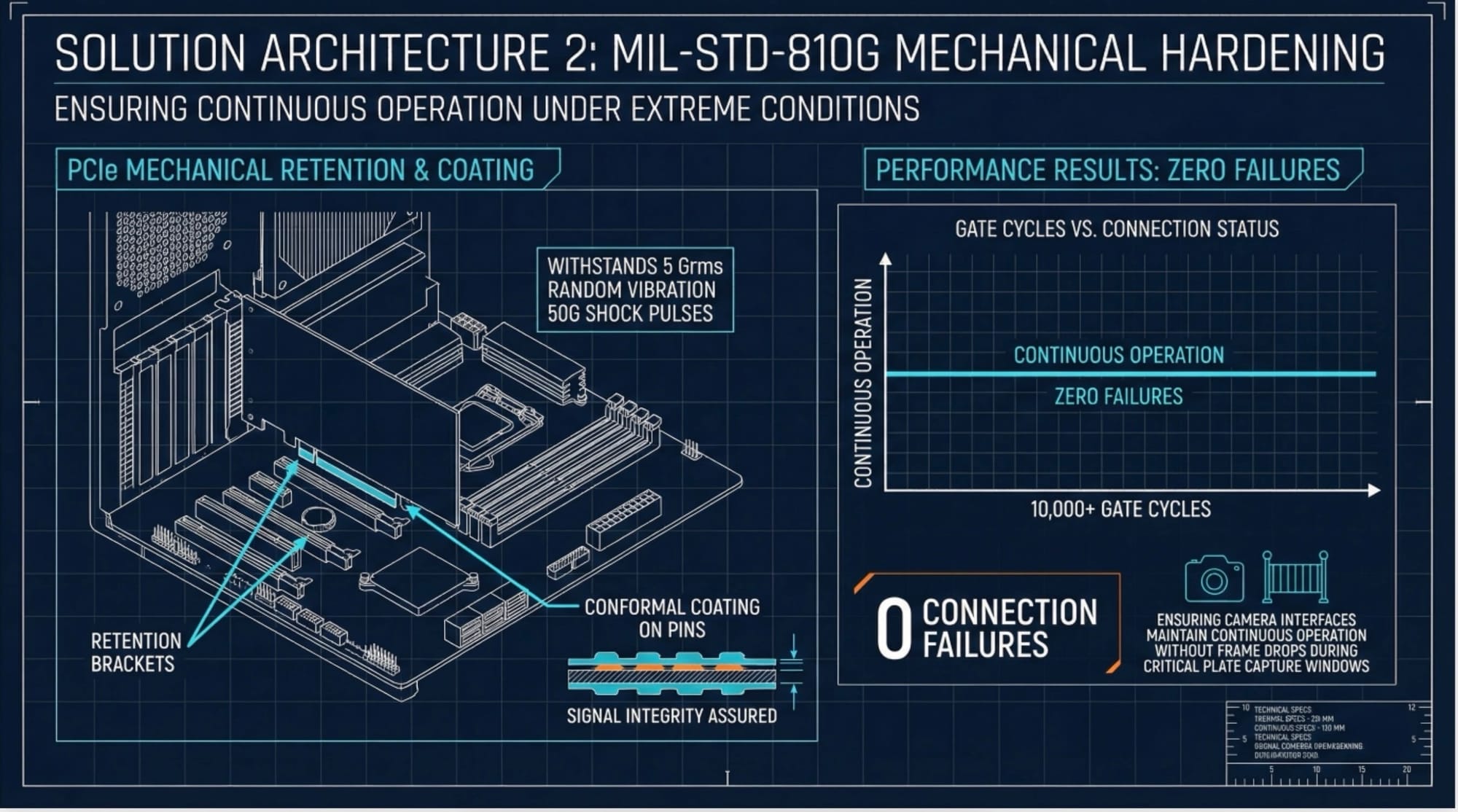
The Architectural Fix: MIL-STD-810G Mechanical Hardening
Compliance with MIL-STD-810G shock and vibration specifications ensures slot retention under operating conditions:
- Mechanism: PCIe slots incorporate mechanical retention brackets and conformal coating on connector pins. Entire assembly withstands 5 Grms random vibration and 50G shock pulses.
Result: Zero connection failures across 10,000+ gate cycles. Camera interfaces maintain signal integrity throughout product lifetime.
3. Dust Ingress: Particulate Contamination in Open Environments
Parking facilities generate airborne particulates from tire rubber, brake dust, and concrete degradation. These particles measure 2-50 microns in diameter and accumulate on thermal surfaces, insulating components from airflow.
The Failure: Ventilated enclosures require filtered air intake. When filters clog with particulate matter, internal pressure drops and thermal resistance increases. Systems overheat despite functioning cooling fans. Maintenance teams must clean filters every 2-4 weeks in high-traffic facilities—a recurring operational cost that approaches 15-20% of annual ownership expense.
The Architectural Fix: IP67-Rated Sealed Chassis
Sealed enclosure design eliminates particle accumulation pathways:
- Mechanism: All I/O connectors use sealed glands with O-ring compression. Chassis achieves IP67 rating with no air exchange required for thermal management.
- Result: No scheduled maintenance for thermal system. Five-year total cost of ownership reduces by 40% compared to filtered ventilation approaches.
Technical Specifications: Parking Management Computing Requirements
| System Requirement | Specification | Engineering Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | -25°C to 70°C | Accommodates seasonal extremes in non-climate-controlled gate enclosures |
| Shock Resistance | 50G, 11ms half-sine pulse | Survives barrier gate impacts and vehicle collisions with gate infrastructure |
| Vibration Tolerance | 5 Grms, 5-500 Hz | Maintains PCIe slot integrity under continuous gate operation |
| Processing Performance | Intel Core i7-9700TE (8 cores, 2.6-4.0 GHz) | Processes 1920×1080 frames at 30 fps for real-time plate recognition |
| Camera Interfaces | 4× GigE Vision ports (PoE) | Supports multi-angle capture for plate visibility under varying vehicle approach angles |
| Mean Time Between Failures | >100,000 hours | Enables five-year deployment without replacement |
Implementation Considerations
Deployment Requirements
| Engineering Advantage (Pros) | Implementation Constraint (Trade-offs) |
|---|---|
| Fanless operation eliminates maintenance cycles - No scheduled filter replacement or fan bearing inspections required over five-year service life | Initial capital cost 30-40% higher than commercial-grade fan-cooled alternatives due to precision machining of thermal chassis |
| MIL-STD-810G certification ensures predictable reliability - Quantified shock/vibration specifications allow accurate failure rate modeling for fleet deployments | System weight increases to 4-6 kg due to aluminum heatsink mass, requiring reinforced mounting in gate enclosures |
| Wide temperature operation without performance throttling - Maintains full processing throughput during summer peak hours when revenue is highest | Thermal design limits processor TDP to 35W - Cannot accommodate high-performance discrete GPUs for advanced AI workloads |
| Sealed IP67 chassis eliminates dust-related failures - Proven reliability in cement plants and mining operations transfers directly to parking applications | All I/O requires sealed connectors - M12 or IP67-rated RJ45 connectors increase cabling cost by 15-20% compared to standard Ethernet |
Related Products
POC-500 Series: Compact DIN-rail mountable platform optimized for gate controller integration. Features ignition power control for energy management during low-traffic periods and CAN bus interface for barrier mechanism control. Ideal for distributed deployments with computing at each gate rather than centralized architecture.
Nuvo-8240GC: GPU-accelerated platform supporting NVIDIA RTX A2000 for facilities requiring AI-based vehicle type classification or parking guidance overlay systems. Maintains fanless operation with 70W GPU TDP while providing 8-lane PCIe Gen4 bandwidth for multi-camera inference workloads.
Contact Us
For technical specifications, product selection assistance, or application engineering support, contact our engineering team at [email protected]. Our engineers can help you choose the right Nuvo Series platform for your specific parking facility requirements.
Visit www.neteon.net for detailed datasheets and technical documentation.