TLDR: Municipal road maintenance teams traditionally required weeks of manual inspection to assess pavement conditions across city networks. A Neousys GC series AI inference platform deployed in intelligent inspection vehicles now processes pavement imagery in real-time, reducing classification time from weeks to seconds while detecting 13 distinct defect types with 93%+ accuracy. The MIL-STD-810G certified system operates continuously at -25°C to 60°C, enabling year-round deployment without thermal throttling.
Overview: The Growing Burden of Pavement Assessment
Road networks form the backbone of urban infrastructure, yet maintaining pavement quality remains a significant operational challenge. The global pavement inspection systems market reached $302 million in 2024, with AI-powered platforms driving a 21% surge in adoption as municipalities seek faster, more consistent assessment methods.
Traditional manual inspection presents multiple engineering constraints. Inspectors must physically walk road segments, subjectively classify damage severity, and manually record findings—a process that introduces inconsistency and extends assessment timelines to weeks or months for metropolitan areas. With over 65% of U.S. roadways requiring periodic condition assessment, transportation agencies face mounting pressure to modernize inspection workflows.
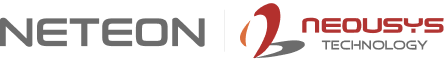
The technical challenge extends beyond simple automation. Any vehicle-mounted inspection system must withstand continuous road vibration (up to 3G RMS), operate across temperature extremes, process high-bandwidth camera feeds in real-time, and maintain reliable cellular connectivity for data transmission—all while delivering inference accuracy comparable to trained human inspectors.
Challenge: Why Consumer-Grade Computing Fails in Mobile Inspection
Deploying AI inference capability inside a moving inspection vehicle presents a compound engineering problem that conventional computing hardware cannot address.
| Requirement | Specification Needed | Challenge with Standard Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | -25°C to 60°C continuous | Commercial systems limited to 0°C to 40°C |
| Shock/Vibration | MIL-STD-810G (3G RMS sustained) | Standard PCs fail at 1G sustained vibration |
| GPU Performance | 120W+ for real-time inference | Laptop GPUs throttle under sustained load |
| Camera Connectivity | PoE + GigE + USB3 (6+ ports) | Consumer systems offer 2-3 ports maximum |
| Power Management | Ignition-controlled startup/shutdown | No automotive power integration |
| Wireless Expansion | 5G/4G + GPS modules | Limited expansion slots |
Thermal management creates the primary bottleneck. Vehicle cabins regularly exceed 50°C during summer operation, yet sustained AI inference generates significant heat from both CPU and GPU. Consumer-grade systems either throttle performance to prevent thermal damage or fail outright under these conditions.
Vibration-induced failures compound the problem. Road surfaces transmit continuous shock and vibration to mounted equipment. Standard PCIe slots, DIMM connectors, and storage interfaces experience micro-disconnections that cause system crashes, data corruption, or hardware damage over time. MIL-STD-810G certification requires sustained operation at 3G RMS—conditions that destroy conventional desktop or server hardware within hours.
I/O density limits camera integration. Intelligent inspection vehicles typically deploy multiple camera angles—downward-facing pavement cameras, forward-looking navigation cameras, and supplementary sensors. Each requires dedicated high-bandwidth connections (PoE for power delivery, GigE for data transfer) that consumer motherboards cannot provide without external hubs that introduce latency and failure points.
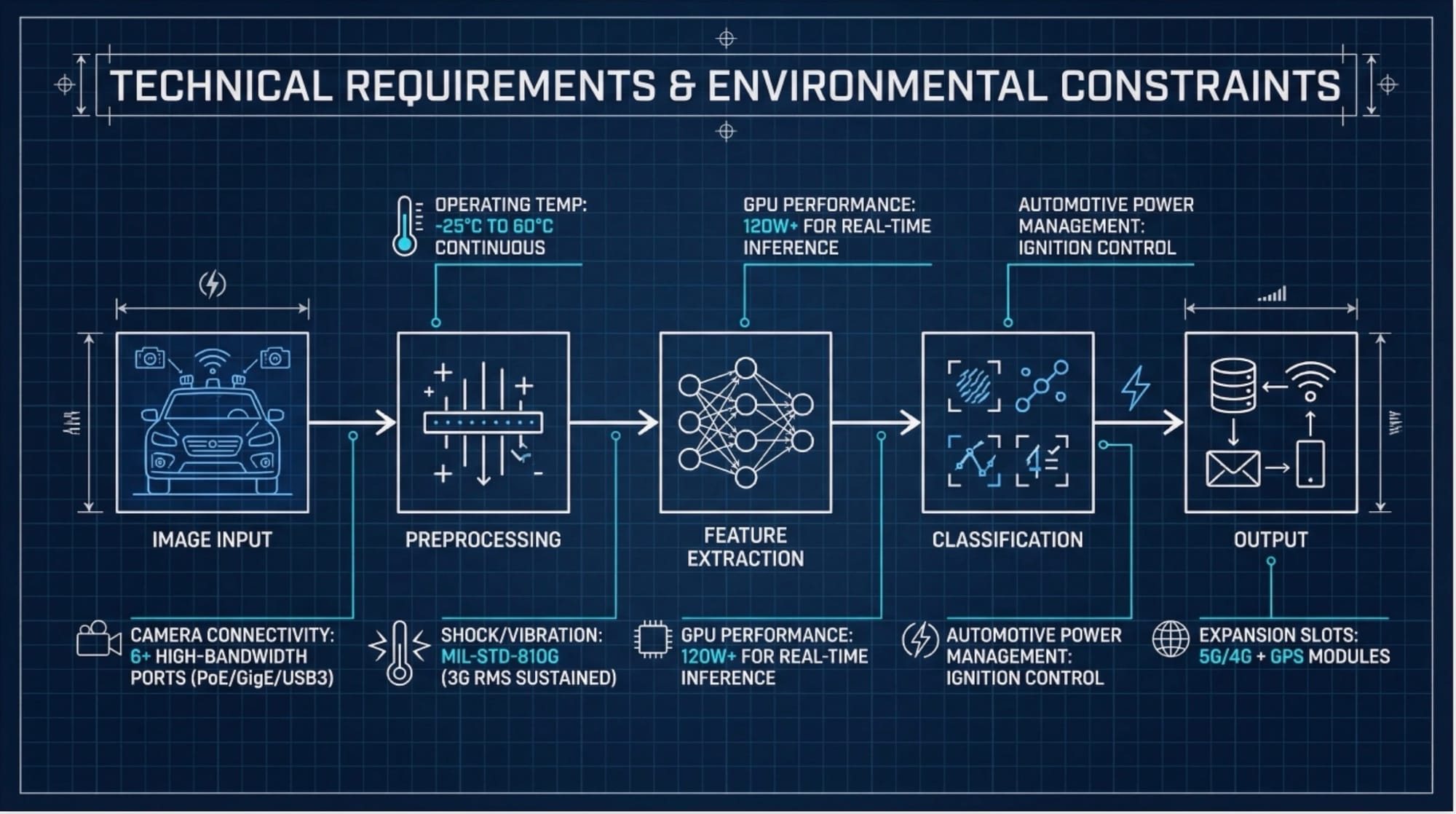
Solution: MIL-STD Certified AI Platform for In-Vehicle Deployment
The Neousys GC series AI inference platform addresses each technical constraint through purpose-built industrial design rather than consumer hardware adaptation.
| Technical Challenge | GC Series Feature | Specification | Engineering Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal throttling | Fanless passive cooling | -25°C to 60°C operation | Zero performance degradation in summer heat |
| Vibration damage | MIL-STD-810G certified chassis | 3G RMS sustained | 100,000+ hour MTBF in mobile deployment |
| GPU performance | Dedicated 120W NVIDIA GTX | Single-precision inference | Real-time classification at driving speed |
| Camera connectivity | Onboard PoE/GigE/USB3 | 6+ high-bandwidth ports | Direct camera connection without external hubs |
| Power cycling | Integrated ignition control | Automotive power management | Safe startup/shutdown with vehicle ignition |
| Data transmission | Mini-PCIe/M.2 expansion | 5G/4G + GPS modules | Real-time upload with precise geolocation |
Performance Data: Manual Inspection vs. GC Series Automated System
The transition from manual visual inspection to AI-powered automated detection delivered measurable improvements across all key metrics:
| Metric | Manual Inspection | GC Series Automated | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment Time (per km) | 45-60 minutes | 12-15 seconds | -99.6% |
| Defect Detection Accuracy | 72% (inspector-dependent) | 93%+ (YOLOv7-based) | +29% |
| Defect Types Identified | 5-7 categories | 13 standardized categories | +86% |
| Consistency (inter-rater) | 68% agreement | 99%+ repeatability | +46% |
| Data Documentation | Manual photography | Automated geotagged capture | N/A |
The accuracy improvement stems from two factors: eliminating human fatigue and subjective interpretation, and leveraging deep learning models trained on expanding databases of pavement imagery collected across multiple inspection vehicles. Each deployment contributes new training data, continuously improving detection capability across the fleet.
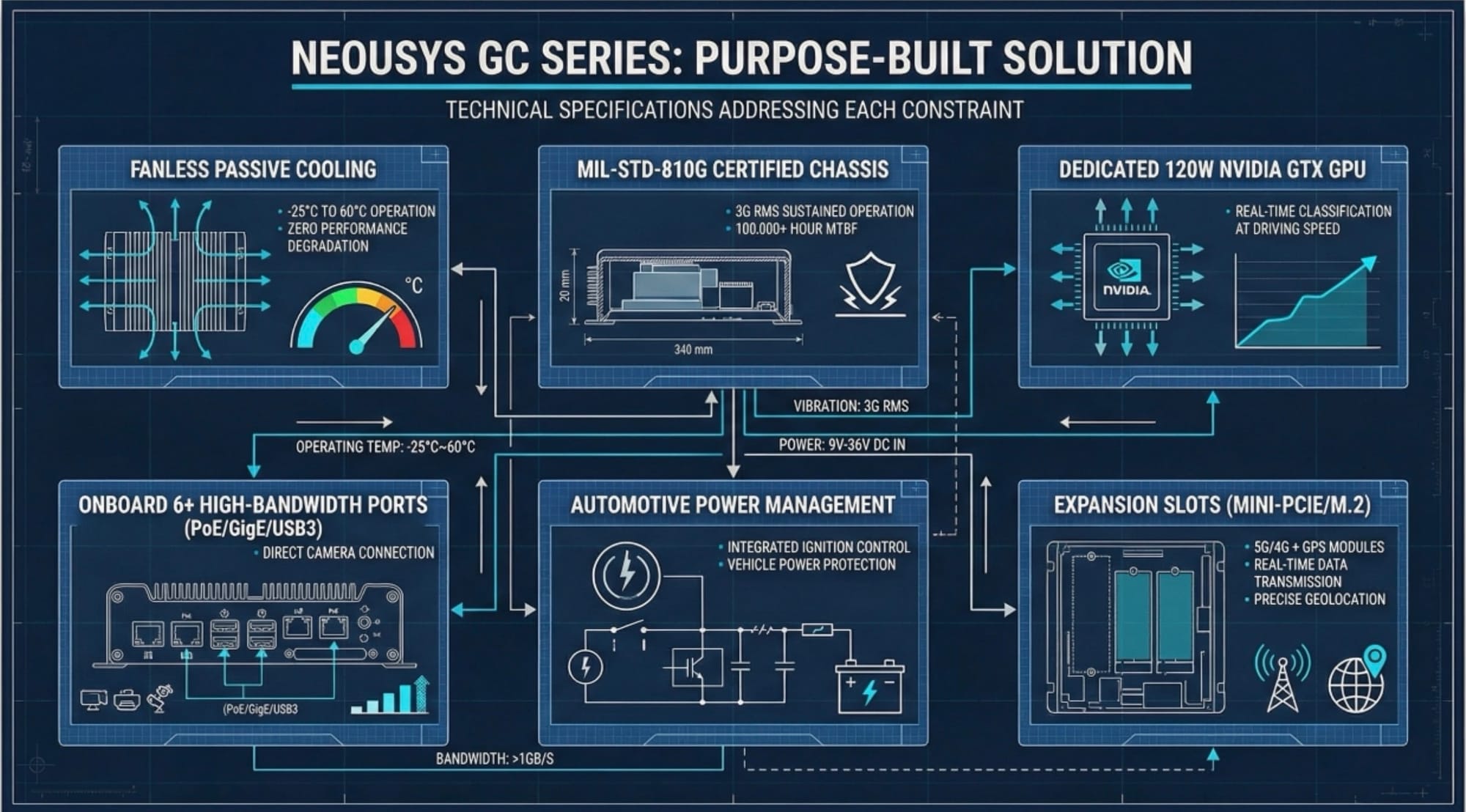
Implementation Architecture
The system captures pavement imagery through vehicle-mounted cameras at normal driving speeds. The GC series platform processes incoming video streams through inference acceleration, classifying detected defects by type (cracks, potholes, rutting, surface deterioration) and severity level. Results transmit via 5G/4G cellular to centralized pavement management systems (PMS), where GPS coordinates enable precise maintenance planning.
Key specifications supporting this workflow:
- Processor: Intel Core with integrated inference optimization
- GPU: NVIDIA GTX 120W with CUDA inference libraries
- Memory: Up to 64GB DDR4 for model loading and frame buffering
- Storage: NVMe SSD for high-speed image caching
- I/O: 6x GigE ports, multiple USB3, PoE capability for camera power
- Expansion: Mini-PCIe and M.2 slots for wireless modules
- Certifications: MIL-STD-810G shock/vibration, E-Mark automotive
Related Products
Nuvo-9160GC: For deployments requiring higher GPU performance, the Nuvo-9160GC supports RTX-class graphics cards up to 130W. Features 13th/12th-Gen Intel Core processors and Neousys' patented Cassette module for simplified GPU installation. Ideal for multi-camera inspection systems requiring simultaneous inference on multiple video streams.
NRU Series: NVIDIA Jetson-based compact platform for space-constrained installations. Delivers edge AI inference with lower power consumption (15-30W) for supplementary detection systems or drone-mounted pavement inspection applications.
Conclusion
Intelligent road inspection vehicles equipped with the GC series platform transform pavement assessment from a labor-intensive manual process into automated, continuous monitoring. The combination of MIL-STD-810G ruggedization, wide-temperature operation, and high-performance GPU inference enables deployment across climate zones without seasonal interruption.
As municipalities expand their inspection coverage, the continuous learning capability—where each vehicle contributes imagery to shared training datasets—promises ongoing accuracy improvements across the global fleet.
For technical specifications and application engineering support, contact our team at [email protected]. Visit www.neteon.net for detailed datasheets and product documentation.